For adults with agitation associated with schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder,
THE EFFECT OF IGALMI WAS EVALUATED IN EXPLORATORY ANALYSES1-4
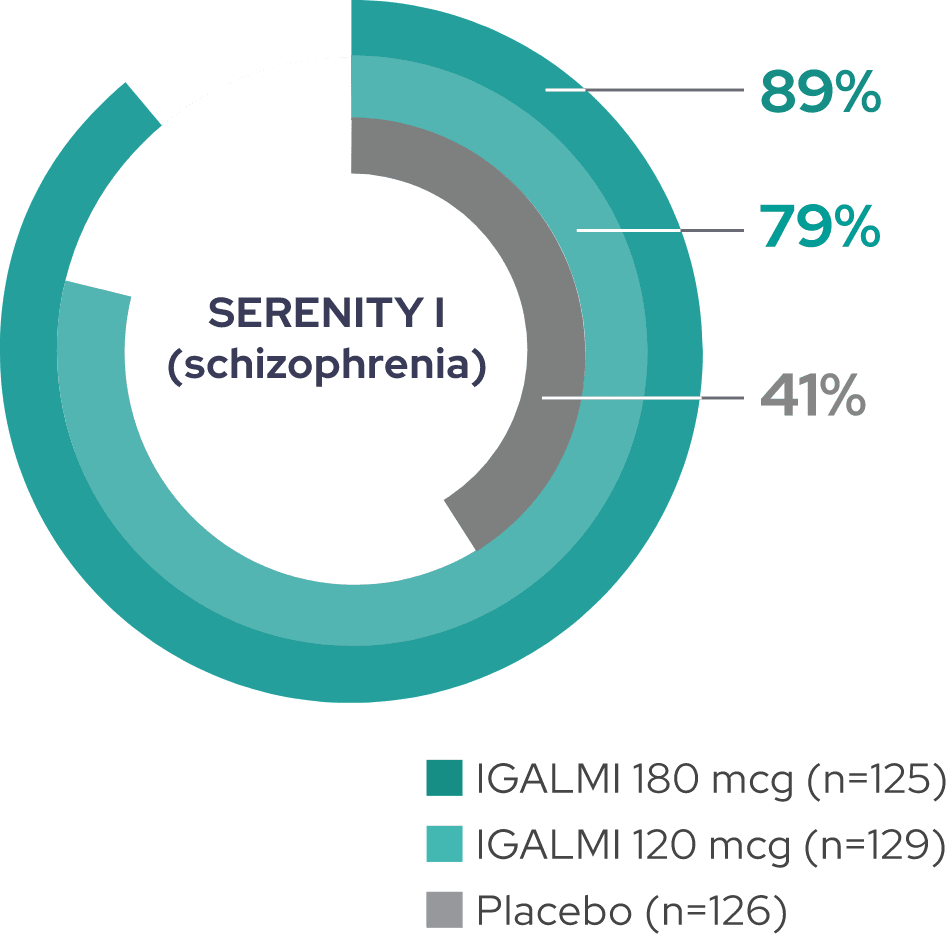
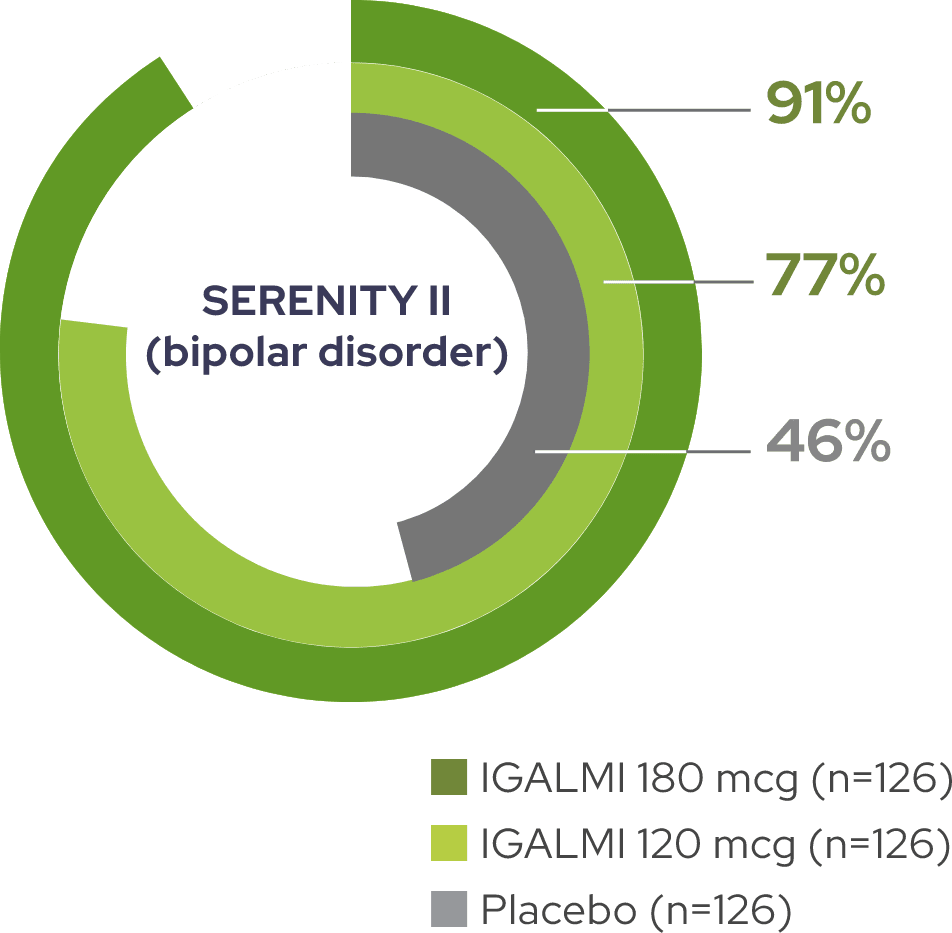
~80 to 90% of patients treated with IGALMI were considered responders1,2
Percentage of PEC responders at 2 hours, defined as achieving a ≥40% reduction in total PEC score


These are exploratory analyses; therefore, the results require cautious interpretation and could represent chance findings.
PEC, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Excited Component.
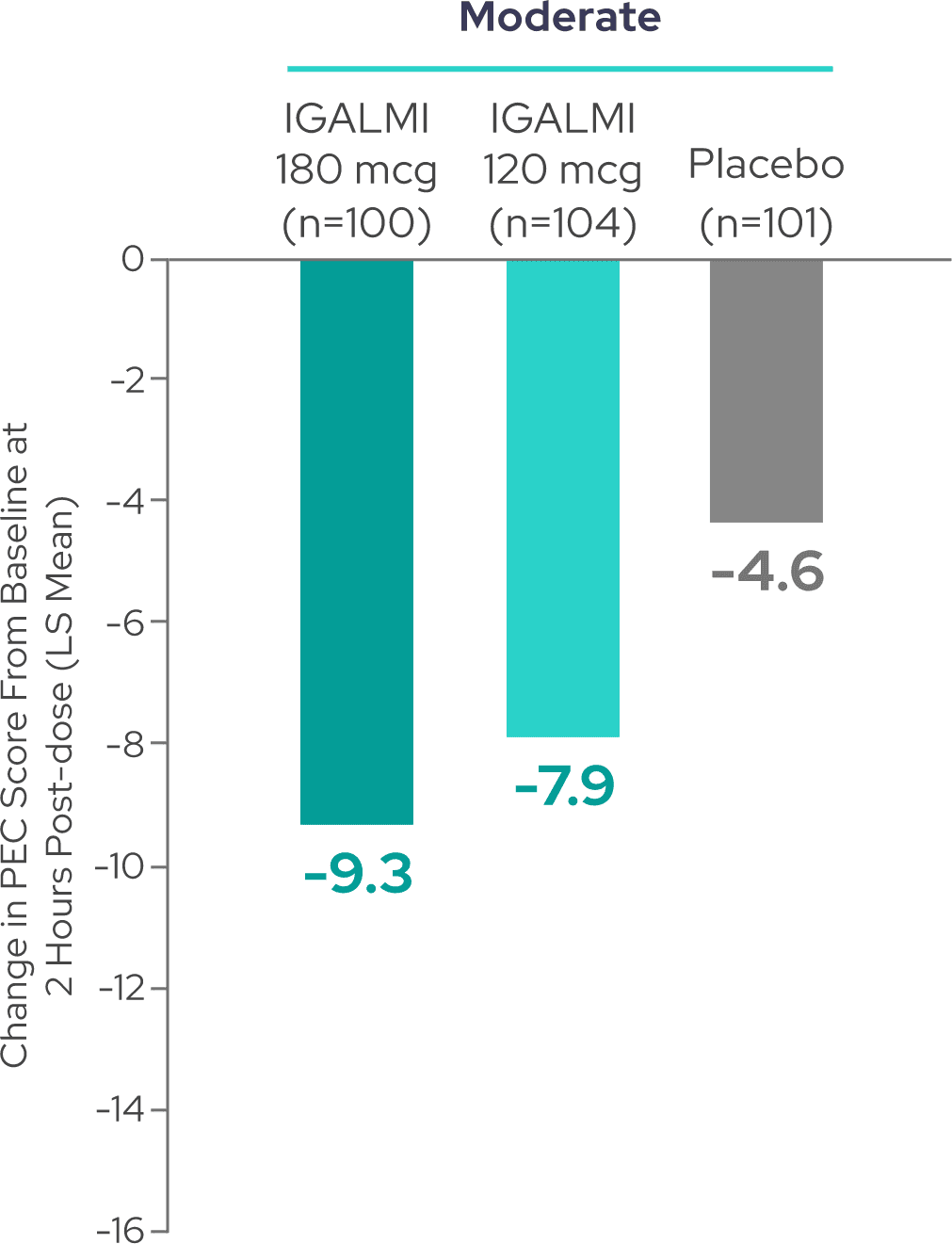
Reductions in PEC score were observed across patients with moderate and severe agitation3

SERENITY I (schizophrenia)
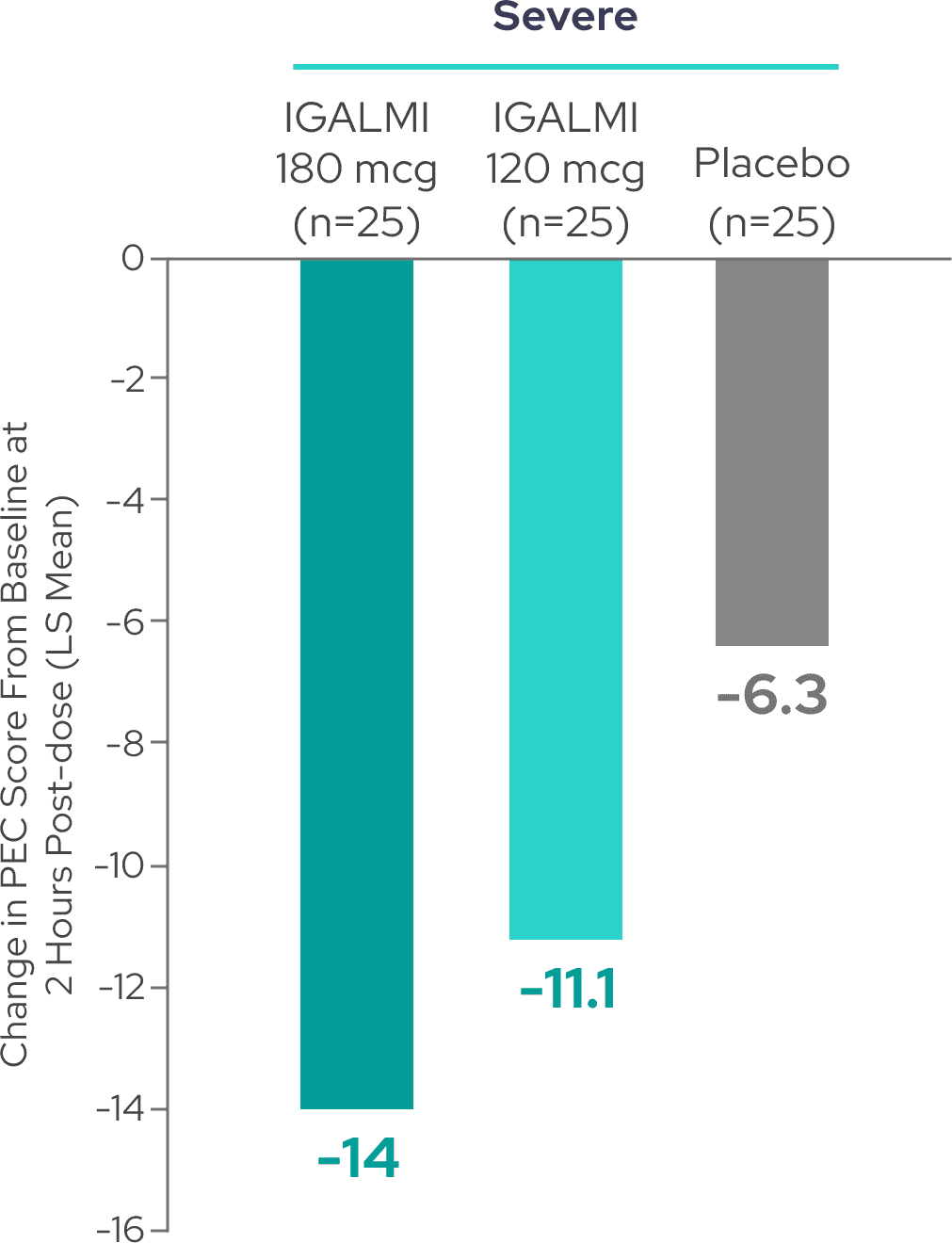
-
80% of patients had moderate agitation
-
20% of patients had severe agitation
SERENITY I (schizophrenia)
SERENITY II (bipolar disorder)
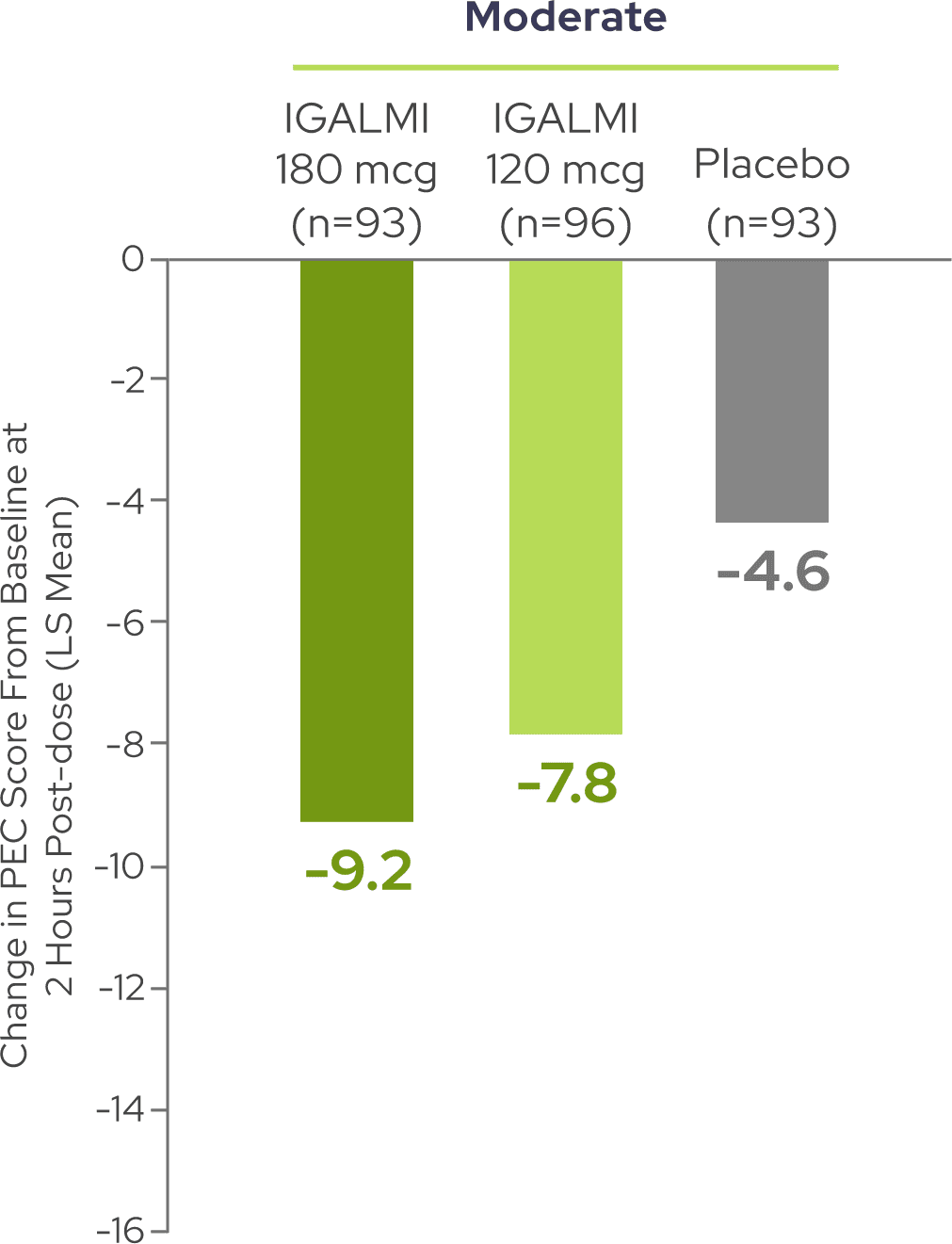
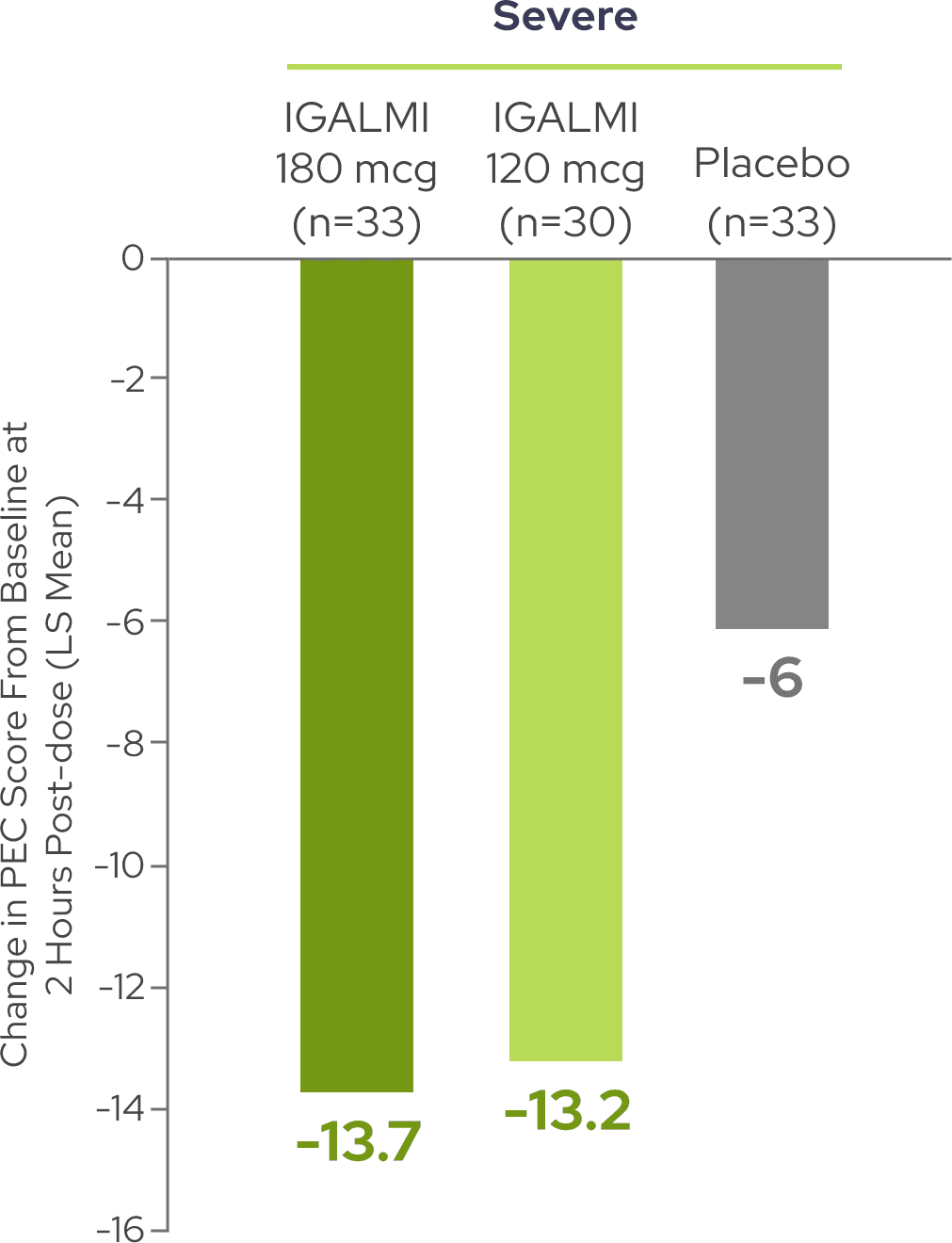
-
75% of patients had moderate agitation
-
25% of patients had severe agitation
SERENITY II (bipolar disorder)
A total PEC score of 14-19 at baseline was considered moderate agitation and a total PEC score of 20-35 at baseline was considered severe agitation.5,6
These are exploratory analyses; therefore, the results require cautious interpretation and could represent chance findings.
Dosage recommendations for IGALMI in adults <65 years of age: administer 120 mcg for mild or moderate agitation or 180 mcg for severe agitation. Refer to full dosage recommendations in the Prescribing Information.7
LS, least squares.
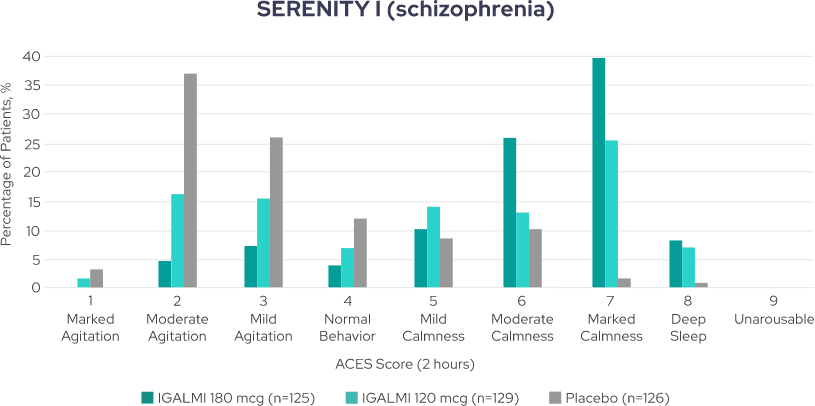
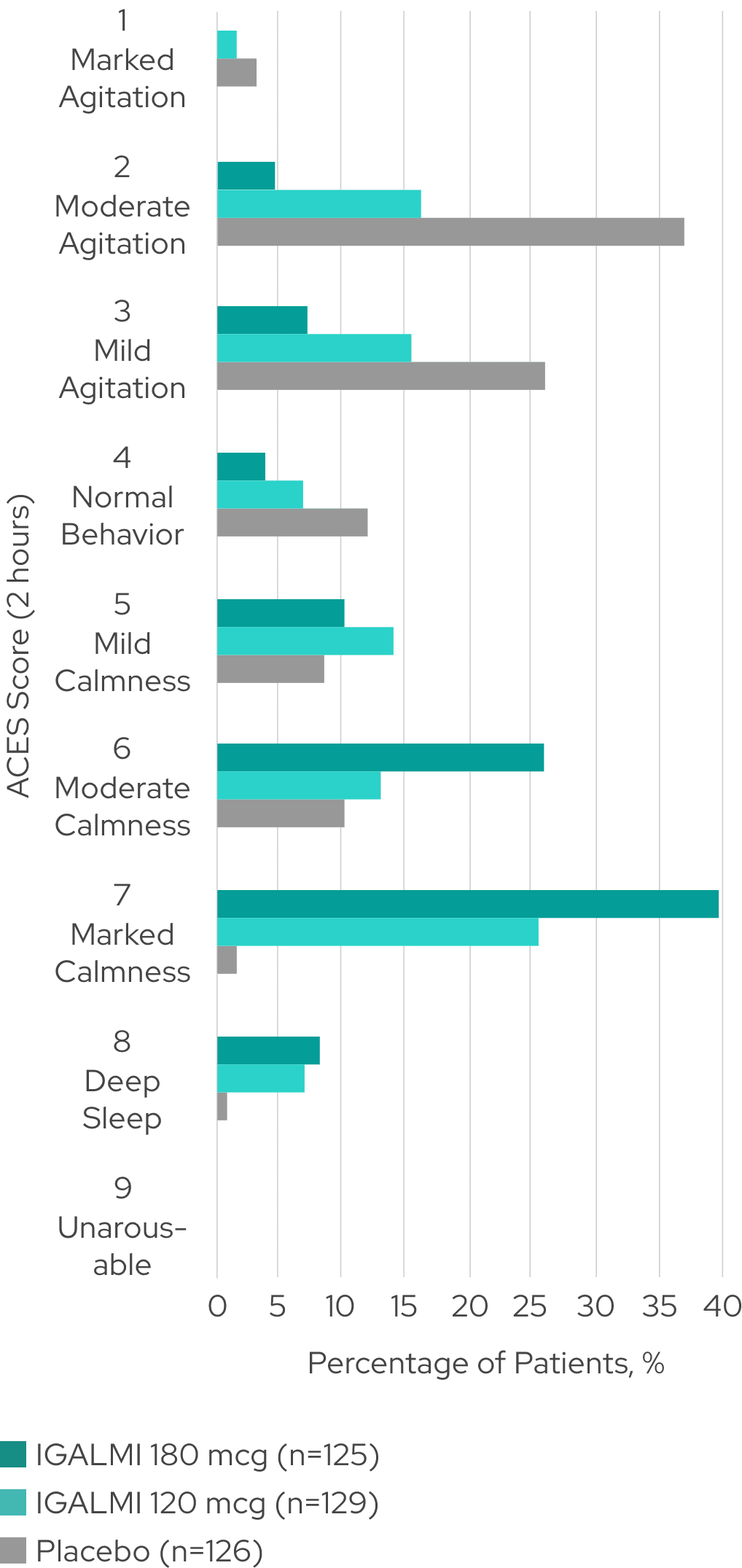
Varying levels of agitation and sedation were assessed using the Agitation-Calmness Evaluation Scale (ACES)1,4,8
Percentage of patients across ACES scores4*
SERENITY I (schizophrenia)
-
All patients were arousable at all ACES time points1,4,8
-
Similar results were seen in SERENITY II (bipolar disorder)4
These are exploratory analyses; therefore, the results require cautious interpretation and could represent chance findings.
*The ACES is a single-item measure rating overall agitation and sedation on a scale from 1 to 9, where 1 indicates marked agitation and 9 indicates unarousable. ACES was performed as an exploratory analysis at baseline (within 15 minutes of the first dose), and 2, 4, and 8 hours post-dose. Resolution of agitation was defined by an ACES score of 4 or higher.1,2
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
INDICATION
See More
Collapse
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
IGALMI is self-administered under the supervision of a healthcare provider. A healthcare provider should monitor vital signs and alertness after IGALMI administration to prevent falls and syncope.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypotension, Orthostatic Hypotension, and Bradycardia: IGALMI causes dose-dependent hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, and bradycardia. In clinical studies with IGALMI, patients were excluded if they had treatment with alpha-1 noradrenergic blockers, benzodiazepines, other hypnotics or antipsychotic drugs four hours prior to study drug administration; had a history of syncope or syncopal attacks; SBP < 110 mmHg; DBP < 70 mmHg; HR < 55 beats per minute; or had evidence of hypovolemia or orthostatic hypotension. Because IGALMI decreases sympathetic nervous system activity, hypotension and/or bradycardia may be more pronounced in patients with hypovolemia, diabetes mellitus, or chronic hypertension, and in geriatric patients. Avoid use of IGALMI in patients with hypotension, orthostatic hypotension, advanced heart block, severe ventricular dysfunction, or history of syncope. After IGALMI administration, patients should be adequately hydrated and should sit or lie down until vital signs are within normal range. If a patient is unable to remain seated or lying down, precautions should be taken to reduce the risk of falls. Ensure that a patient is alert and not experiencing orthostatic hypotension or symptomatic hypotension prior to allowing them to resume ambulation.
INDICATION
IGALMI is indicated for the acute treatment of agitation associated with
schizophrenia or bipolar I or II disorder in adults.
Limitations of Use: The safety and effectiveness of IGALMI have not been established beyond 24 hours from the first dose.
QT Interval Prolongation: IGALMI prolongs the QT interval. Avoid use of IGALMI in patients at risk of torsades de pointes or sudden death, including those with known QT prolongation, a history of other arrhythmias, symptomatic bradycardia, hypokalemia, or hypomagnesemia, and in patients receiving other drugs known to prolong the QT interval.
Somnolence: IGALMI can cause somnolence. Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or operating hazardous machinery, for at least eight hours after taking IGALMI.
Risk of Withdrawal Reactions, Tolerance, and Tachyphylaxis: IGALMI was not studied for longer than 24 hours after the first dose. There may be a risk of physical dependence, a withdrawal syndrome, tolerance, and/or tachyphylaxis if IGALMI is used in a manner other than indicated.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and at least twice the rate of placebo) were somnolence, oral paresthesia or oral hypoesthesia, dizziness, dry mouth, hypotension, and orthostatic hypotension.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drugs That Prolong the QT Interval: Avoid use. Concomitant use of drugs that prolong the QT interval may add to the QT-prolonging effects of IGALMI and increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmia.
Anesthetics, Sedatives, Hypnotics, and Opioids: Concomitant use may cause enhanced CNS-depressant effects. Reduction in dosage of IGALMI or the concomitant medication should be considered.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Hepatic Impairment and Geriatric Patients (≥65 years old): A lower dose is recommended in patients with hepatic impairment and geriatric patients. See the full Prescribing Information for the recommended dosage depending on the agitation severity.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc. at 1-833-201-1088 1-833-201-1088 or medinfo@bioxceltherapeutics.com, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-10881-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
References:
1. Data on file. BXCL501-301 CSR (SERENITY I). BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc.; January 2021. 2. Preskorn SH, Zeller S, Citrome L, et al. Effect of sublingual dexmedetomidine vs placebo on acute agitation associated with bipolar disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2022;327(8):727-736. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.0799 3. Data on file. BXCL501-301 & -302 PEC change from baseline by agitation severity at baseline (SERENITY I and II). BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc.; April 2021. 4. Data on file. BXCL501-301 & -302 ACES distribution (SERENITY I and II). BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc.; March 2022. 5. Montoya A, Valladares A, Lizán L, San L, Escobar R, Paz S. Validation of the excited component of the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS-EC) in a naturalistic sample of 278 patients with acute psychosis and agitation in a psychiatric emergency room. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2011;9(18):1-11. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-9-18 6. Martinez-Raga J, Amore M, Di Sciascio G, et al. 1st international experts’ meeting on agitation: conclusions regarding the current and ideal management paradigm of agitation. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9:54. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00054 7. IGALMI. Package insert. BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc.; 2022. 8. Data on file. BXCL501-302 CSR (SERENITY II). BioXcel Therapeutics, Inc.; January 2021.

